From eight weeks till 14 years outdated, the NHS recommends plenty of vaccines for youngsters and youngsters.
The well being service says immunisations are one of the best defence in opposition to probably critical diseases, and it’s important they’re given on the appropriate time.
Listed here are all of the vaccinations youngsters are really useful to have, at what age and what they shield in opposition to.
Infants underneath one yr outdated
At eight weeks, infants are really useful to have the next jabs:
• 6-in-1 vaccine• Rotavirus vaccine• MenB vaccine
The 6-in-1 vaccine protects in opposition to the next diseases:
• Diphtheria – a contagious an infection that impacts the nostril and throat, and typically the pores and skin;• Hepatitis B – a liver an infection that’s unfold by means of blood, semen and vaginal fluids;• Haemophilus influenzae kind b (referred to as Hib) – a kind of micro organism that may trigger life-threatening infections;• Polio – a virus that spreads simply from individual to individual and may trigger signs that have an effect on the mind and nervous system;• Tetanus – a life-threatening situation brought on by micro organism getting right into a wound;• Whooping cough – an an infection of the lungs and respiratory tubes that spreads simply.
The rotavirus vaccine helps shield in opposition to rotavirus, a standard explanation for diarrhoea and vomiting that may be quite common in youngsters and younger infants.
The MenB vaccine can shield in opposition to a micro organism referred to as meningococcal group B that may trigger critical diseases, together with meningitis and sepsis.
A second dose of all three of the above is run once more at 12 weeks outdated.
When a child reaches 16 weeks, the NHS recommends a 3rd dose of the 6-in-1 vaccine, in addition to the Pneumococcal vaccine.
This helps shield in opposition to critical diseases like:
• Meningitis – an an infection within the mind and spinal wire;• Sepsis – a life-threatening response to an an infection;• Pneumonia – an an infection within the lungs.
Youngsters aged one to a few
At one yr, the NHS recommends infants have their first MMR vaccine.
This provides long-term safety in opposition to:
• Measles – an an infection that causes a rash and flu-like signs;• Mumps – an an infection that causes painful swelling on the cheeks and neck;• Rubella – sometimes called German measles, and may trigger a rash over the physique.
As of January 2026, infants aged between 12 and 18 months will even get the varicella vaccine, which protects in opposition to chickenpox.
The varicella vaccination might be mixed with the MMR vaccine, making it the MMRV.
Picture:
Chickenpox an infection
The vaccine offers round 98% safety in youngsters and about 75% safety in adults after two doses, and is predicted to guard round 500,000 infants yearly when rolled out by the NHS.
The well being service additionally recommends youngsters having the next vaccines on the age of 1:
• A second dose of the Pneumococcal vaccine;• A 3rd dose of the MenB vaccine.
For infants born earlier than 30 June 2024, the NHS recommends a Hib/MenC vaccine on the age of 1. This protects in opposition to hib and meningitis C.
As a result of Hib/MenC vaccine being discontinued, when infants born after 1 July 2024 attain 18 months outdated, they’re provided:
• A fourth dose of the 6-in-1 vaccine;• A second MMR vaccine.
When do adults want vaccines?
Like infants and youngsters of a sure age, these aged 65 and over are additionally really useful vaccinations.
The NHS affords the flu vaccine yearly to these over 65.
The shingles vaccine can also be provided to those that turned 65 on or after 1 September 2023, and to these aged 70-79.
For 75 to 79 -year-olds, the RSV vaccine is really useful. This helps shield in opposition to respiratory syncytial virus, which might trigger pneumonia and bronchiolitis in older or youthful folks.
Folks aged 75 and over are additionally provided the COVID-19 vaccine. Sometimes, vaccines in opposition to coronavirus are provided within the spring and winter.
On the age of two, the NHS recommends:
• A flu vaccine.
It says flu can unfold simply amongst youngsters, and vaccinating them helps shield others who’re at greater threat of getting significantly in poor health.
It’s provided once more to:
• Youngsters aged three;• Faculty youngsters from reception to yr 11;• From the age of six months to 17 years to these with sure long-term well being situations.
At three years and 4 months outdated, a second dose of MMR is really useful for youngsters born on or earlier than 30 June 2024.
The 4-in-1 faculty booster vaccine can also be provided.
This helps shield in opposition to diphtheria, polio, whooping cough and tetanus and is given to youngsters earlier than they begin faculty.
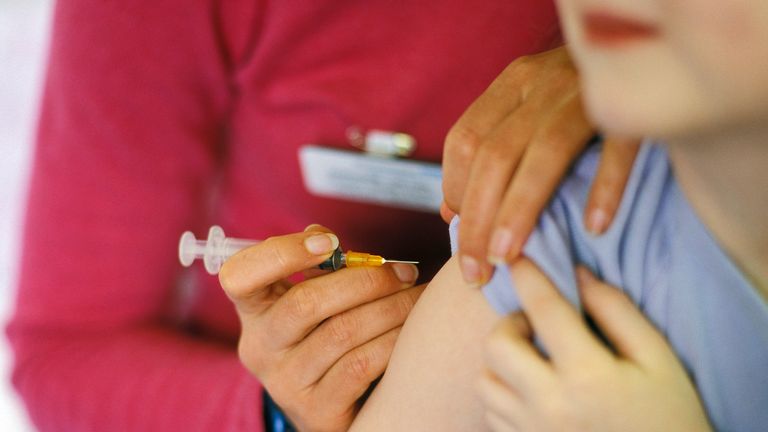
Picture:
File pic: iStock
Youngsters aged 12-14
From 12 to 13, youngsters are provided the HPV vaccine, which helps shield in opposition to human papillomavirus, a standard virus that is unfold by means of pores and skin contact.
Ladies underneath 25 and boys born after 1 September 2006 who missed having the vaccine in school also can get the vaccine by means of their GP.
Pregnant? You can additionally want vaccinations
The NHS recommends the next to those that are pregnant:
• A flu vaccine throughout flu season (October to March within the UK)
• A whooping cough vaccine at 20 weeks pregnant
• An RSV vaccine at 28 weeks pregnant
At 14 years outdated, the NHS recommends the next:
• Td/IPV vaccine (3-in-1 teenage booster) – this helps shield in opposition to tetanus, diphtheria and polio. It is really useful for youngsters in yr 9 in school, and people at greater threat of the diseases;• MenACWY vaccine – this helps shield in opposition to meningitis and sepsis.
Whereas infants are given the MenB vaccine to assist shield in opposition to a standard kind of micro organism that causes meningitis, the MenACWY vaccine helps shield in opposition to 4 different sorts of micro organism linked to the virus.
Missed a vaccination?
The NHS says to contact your GP should you assume you or your youngster has missed any vaccinations.
Most immunisations may be taken after the really useful age.
Some infants and youngsters can also require additional vaccines if they’re prone to a specific sickness or have an underlying well being situation.
People who have had a critical allergic response to any vaccination or are allergic to any of the substances won’t obtain it.







